Neural therapy according to Huneke: origin and development
Developed by the brothers Ferdinand and Walter Huneke, neural therapy has proven itself as a holistic diagnostic and therapeutic method in the treatment of acute as well as chronic pain.

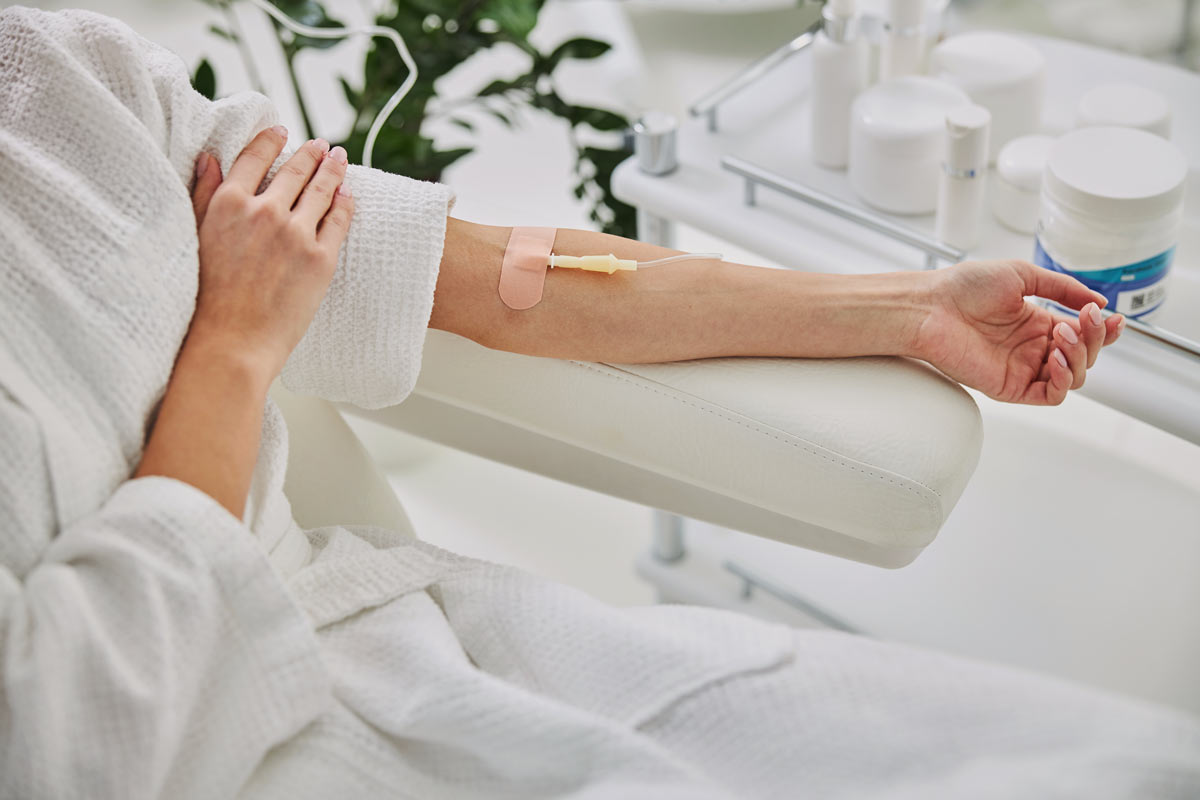
The aim of this pain therapy is to stimulate the body’s self-healing powers by injecting a local anesthetic. In the course of a successful treatment cycle, the discomfort decreases after each intervention, up to complete freedom from pain. How did this form of therapy, how exactly does neural therapy according to Huneke and when is it used?.
Evolution of neural therapy
The brothers and physicians Ferdinand and Walter Huneke discovered the healing effect of procaine in 1925.
When his sister suffered from a migraine attack, Ferdinand Huneke injected her with the anesthetic, as it is now believed accidentally. He noticed that the headache attack was shortened in this way. The Huneke brothers then continued to develop this pain therapy by injecting procaine, and in 1940 Ferdinand discovered the so-called “seconds phenomenon” – a spontaneous, short-lived freedom from symptoms after the injection. As a reminiscence of their discoverers, the pain therapy is now called neural therapy according to Huneke..
For what complaints can neural therapy be used?
Most often, neural therapy treatment is safely applied as pain therapy, both chronic and acute pain. These include, for example:
- headaches and migraines
- back pain
- postoperative pain
However, the possible applications of this form of therapy are diverse. Other indications for neural therapy treatment:
- Movement restrictions and joint disorders (eg. Shoulder-arm syndrome, discomfort in the knee, elbow or hip joint)
- Infections
- (Chronic) inflammation of the respiratory tract, eyes, bladder, etc.
- Disorders in hormone balance
- Hypertension and circulatory disorders
- Heart problems such as shortness of breath, palpitations, and arrhythmias
- dizziness
- Exhaustion states such as sleep disorders or burnout
- Post-traumatic stress disorder and depressive episodes
- Ear noise (tinnitus)
- Wound healing disorders and poorly healed scars
How does neural therapy work?
In a healthy organism, the body’s own regulatory system is able to compensate for minor dysfunctions. However, if major disturbances occur, this self-regulation becomes unbalanced. Neural therapy treatments aim to mobilize the self-healing powers and bring the autonomic nervous system back into balance..
The holistic approach of neural therapy assumes that scars, chronic inflammation and other disease patterns act as foci or interference fields that can trigger pain in other parts of the body. By applying stimuli and stimulating such interference fields with the aid of locally acting anesthetics, certain nerve connections are briefly interrupted or “switched off”. Administering small amounts of anesthetics suppresses the transmission of excitation and reduces pain. During this “relaxation phase” the body gets the chance to regulate out of balance control circuits themselves new and thus normalize..
In a neural therapeutic treatment, a locally acting anesthetic is injected at interference fields, scars, pain or reflex points.